What is A2P messaging?
A2P messaging helps businesses send automated messages to consumers. Learn more about A2P messaging and its use cases.
A2P (application-to-person) messaging is a type of SMS text messaging used to send messages from an application or software program to a mobile device or phone. As this method of communication is largely used by companies and organizations to communicate with customers and subscribers, A2P messaging is also often referred to as business SMS. Consumers will typically encounter A2P messages in the form of appointment reminders, order status updates or promotional messages.
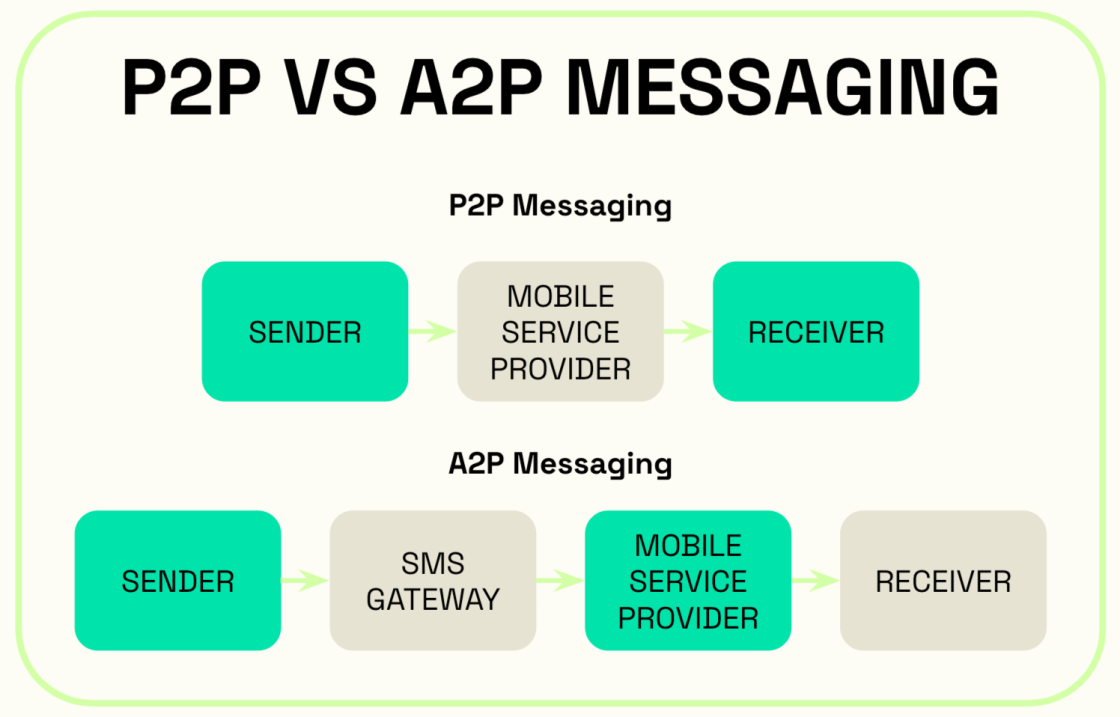
How is A2P messaging different from P2P messaging?
The main difference between P2P (person-to-person) and A2P messaging is the origin of the messages in question. While a P2P message is sent from one person to another, an A2P SMS is an automated text sent via a messaging platform (application) to the recipient. But here’s the twist:
All messages sent from a business—even if they’re sent by an individual and not an automated system—are considered A2P messages.
As such, organizations must ensure that their messages comply with the Telephone Consumer Protection Act (TCPA). The TCPA protects consumers from unwanted or unsolicited communication from businesses. There are multiple guidelines laid out by TCPA, but to summarize, organizations should:
- Get written consent from consumers before beginning communications.
- Provide clear ways for consumers to opt in or out of messages.
- Include the organization’s name in each message.
- Respect opt-outs and the Do Not Call Registry.
Check out our SMS compliance guide and checklist for more information on text messaging regulations.
What number types can you use with A2P messaging?
A2P messaging supports a range of number types depending on the messaging platform and the country where the numbers are used. In general, the most common number types used for A2P messaging include:
- Short codes are typically four- or five-digit numbers used for sending and receiving text messages. They’re often used for marketing campaigns, voting, or other interactive messaging services.
- Long codes are regular phone numbers that can be used for A2P messaging. They’re often used by businesses for two-way messaging, such as customer support and order tracking.
- 10DLC numbers are 10-digit phone numbers specifically designed for A2P messaging. They’re vetted by carriers to ensure compliance with industry standards and best practices, and they offer higher messaging throughput than long code numbers. Carrier vetting means messages sent from 10DLC numbers are more likely to be delivered quickly and reliably. In addition, 10DLC numbers offer more advanced messaging features, such as message templates, which can help businesses ensure compliance with carrier requirements and industry regulations.
- Toll-free numbers start with specific codes, such as 800, 888, or 877. They’re often used for customer support, marketing campaigns, and other A2P messaging services.
- Virtual phone numbers aren’t tied to a specific physical phone line. They’re often used for A2P messaging in countries where short codes and long codes are not available.
- Sender IDs are alphanumeric strings that identify the sender of a message. Like virtual numbers, they’re often used for A2P messaging services in countries where short codes and long codes are not available.
What are some A2P messaging use cases?
According to a recent report from Beyond Market Insights, the A2P SMS market is expected to grow from 62.2 billion in 2021 to 89.2 billion in 2030. That growth is largely due to the saturation of other channels such as email or social media and the relative cost-effectiveness of SMS communication.
Below are a few of the main ways your organization could leverage A2P messaging to communicate with customers, subscribers or prospects.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
MFA or two-factor authentication (2FA) are security methods used by many organizations to verify identities and prevent fraud. A 2FA message typically includes a one-time pin, code or link sent to a recipient’s phone to verify their account or a login attempt.
In industries with strict security regulations, such as finance or healthcare, MFA or 2FA technology is often required to access certain accounts or information.
Important alerts and updates
Organizations can also send an automated SMS to update customers about the status of their order or remind them of an upcoming appointment or reservation. These types of messages typically include a package tracking number, a link to an original order or a request to confirm an appointment time.
Even government entities use SMS to communicate with people. In the U.S., the Emergency Alert System (EAS) allows the President to alert Americans to national emergencies.
Marketing messages
On average, people receive around 100 emails per day—and nearly half of them are spam. To reach customers through a more personal, less saturated channel, more organizations are turning to SMS to conduct marketing campaigns and provide better customer service.
Compared to email, SMS also has a higher click-through rate (CTR). While nearly 20% of people will click a link sent in a text message, not even 4% of people will click a link received in an email.
Make sure your important messages reach their destinations
A2P messaging seems simple—find a messaging platform or set up a business phone and start texting your customers. However, the reality is more complex.
Compliance is the biggest reason that businesses need to choose a trusted provider for their A2P messaging. TCPA violators can be fined $500–$1,500 per non-compliant text. That’s a hefty fee for even one rogue SMS. But if you’re a business sending thousands of messages per day, you could be looking at a million-dollar fine.
And if you’re investing in SMS communications to send important messages like appointment reminders or 2FA codes, you’ll want to make sure that you’re sending them over a reliable network. Sending undelivered texts into the theoretical void doesn’t do your business—or your customers—any good.